lv dysfunction | what is lv systolic dysfunction lv dysfunction Learn what left ventricular dysfunction is, how it can be diagnosed and treated, and how a smartwatch can help detect it. Dr. Paul Friedman, a Mayo Clinic cardiologist, answers . $8,480.00
0 · what is severe lv impairment
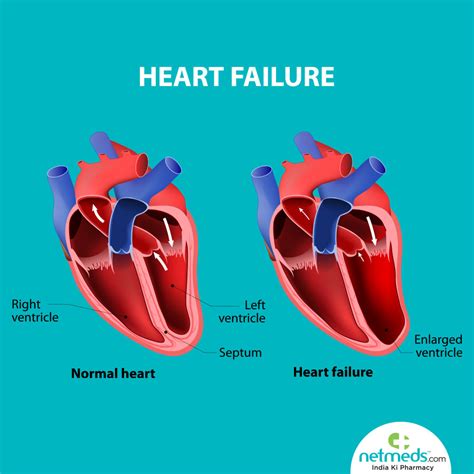
1 · what is lv systolic dysfunction
2 · what does lv dysfunction mean
3 · lv dysfunction treatment
4 · lv dysfunction symptoms
5 · lv dysfunction grades
6 · life expectancy with diastolic dysfunction
7 · is 10 lv dysfunction
$16K+
Learn about left-sided heart failure, a condition where the heart can't pump blood effectively. Find out the types, causes, diagnosis, treatment and prevention options for this serious disease. This article reviews the aetiologies, pathophysiology, and treatment of left ventricular dysfunction (LVD) and congestive heart failure (CHF). It also discusses the role of . Learn about the causes, symptoms, complications and treatment of left ventricular hypertrophy, a condition that thickens the walls of the lower left heart chamber. Find out how to prevent and manage this heart problem that . Learn what left ventricular dysfunction is, how it can be diagnosed and treated, and how a smartwatch can help detect it. Dr. Paul Friedman, a Mayo Clinic cardiologist, answers .
As demonstrated by AlJaroudi et al, echo-Doppler progression of diastolic dysfunction can detect LV dysfunction at an early stage and indicates increased risk for future . Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) is a condition that affects your heart’s ability to fill up with blood before sending the blood out into your circulation. Your heartbeat has.
Left-sided heart failure affects the heart’s ability to pump blood. It includes diastolic dysfunction and systolic heart failure.Left ventricular dysfunction (LVD) with subsequent congestive heart failure (CHF) constitutes the final common pathway for a host of cardiac disorders. Coronary artery narrowing or ischaemic heart disease is the dominant cause of heart failure and is often associated with acute or prior myocardial infarction.
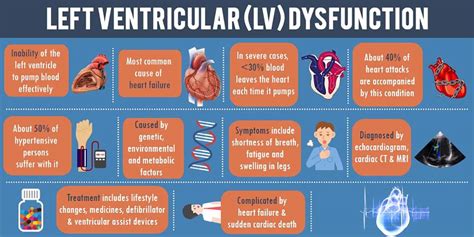
Uncontrolled high blood pressure is the most common cause of left ventricular hypertrophy. Complications include irregular heart rhythms, called arrhythmias, and heart failure. Treatment of left ventricular hypertrophy depends on the cause. Treatment may include medications or surgery. Left ventricular dysfunction is the medical name for a weak heart pump. It's a condition that impacts about 9% of people over the age of 60, which is around 7 million Americans. In this Mayo Clinic Minute, Dr. Paul Friedman, a Mayo Clinic cardiologist, explains what the condition is and how it can be diagnosed and treated. As demonstrated by AlJaroudi et al, echo-Doppler progression of diastolic dysfunction can detect LV dysfunction at an early stage and indicates increased risk for future events. This is a fertile area for continued important advances.
Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement that represents the percentage of blood the left ventricle pumps out with every contraction. It’s a sign of how well your heart is pumping blood. The normal, healthy range for EF measurement is 55% to 70%. An EF under 40% may indicate systolic heart failure. The most common etiologies of left heart failure are coronary artery disease and hypertension. The latter can cause left heart failure through left ventricular hypertrophy (leading to HFpEF), and also serves as a risk factor for coronary artery disease (which can lead to HFrEF). Diastolic heart failure, also known as heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), is a condition in which your heart’s main pumping chamber (left ventricle) becomes stiff and unable to fill properly.
To diagnose left ventricular hypertrophy, a healthcare professional does a physical exam and asks questions about your symptoms and family's health history. The care professional checks your blood pressure and listens to your heart with a device called a stethoscope. Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) is a condition that affects your heart’s ability to fill up with blood before sending the blood out into your circulation. Your heartbeat has.
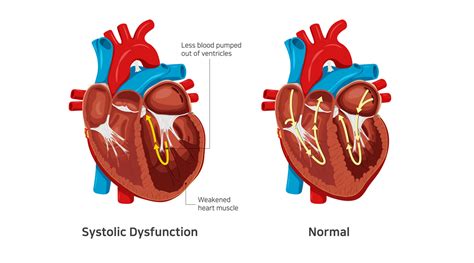
Left-sided heart failure affects the heart’s ability to pump blood. It includes diastolic dysfunction and systolic heart failure.
Left ventricular dysfunction (LVD) with subsequent congestive heart failure (CHF) constitutes the final common pathway for a host of cardiac disorders. Coronary artery narrowing or ischaemic heart disease is the dominant cause of heart failure and is often associated with acute or prior myocardial infarction. Uncontrolled high blood pressure is the most common cause of left ventricular hypertrophy. Complications include irregular heart rhythms, called arrhythmias, and heart failure. Treatment of left ventricular hypertrophy depends on the cause. Treatment may include medications or surgery. Left ventricular dysfunction is the medical name for a weak heart pump. It's a condition that impacts about 9% of people over the age of 60, which is around 7 million Americans. In this Mayo Clinic Minute, Dr. Paul Friedman, a Mayo Clinic cardiologist, explains what the condition is and how it can be diagnosed and treated.
what is severe lv impairment
As demonstrated by AlJaroudi et al, echo-Doppler progression of diastolic dysfunction can detect LV dysfunction at an early stage and indicates increased risk for future events. This is a fertile area for continued important advances.
Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement that represents the percentage of blood the left ventricle pumps out with every contraction. It’s a sign of how well your heart is pumping blood. The normal, healthy range for EF measurement is 55% to 70%. An EF under 40% may indicate systolic heart failure. The most common etiologies of left heart failure are coronary artery disease and hypertension. The latter can cause left heart failure through left ventricular hypertrophy (leading to HFpEF), and also serves as a risk factor for coronary artery disease (which can lead to HFrEF). Diastolic heart failure, also known as heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), is a condition in which your heart’s main pumping chamber (left ventricle) becomes stiff and unable to fill properly.
what is lv systolic dysfunction
$6,650.00
lv dysfunction|what is lv systolic dysfunction